
Key Takeaways from the 2023 GIPS® Standards Conference
Sean P. Gilligan, CFA, CPA, CIPM
October 25, 2023

CFA Institute hosted the 27th annual GIPS Standards Conference on October 17th – 18th 2023 in Chicago, Illinois. As expected, it was filled with a lot of familiar faces, but also had quite a few first timers, which was nice to see.
Being almost a year into the SEC Marketing Rule and with implementation of the Private Fund Adviser Quarterly Statement Rule on the horizon, the hottest topics of this year’s conference were the sessions relating to regulatory compliance. These sessions included discussions with representatives from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) answering practical questions related to adherence to these rules as well as sessions with senior performance professionals discussing the detailed performance methodology required to comply.
Other topics included a review of the proposed guidance statement for applying the GIPS standards to OCIOs, helpful advice for updating consultant databases, a proposed method to risk-adjust performance attribution, and some lessons on soft skills for leaders managing relationships.
SEC Marketing Rule
Michael McGrath, CFA, Partner with Dechert LLP and Robert Shapiro, Assistant Director, Division of Investment Management with the SEC together with Karyn Vincent, CFA, CIPM and Krista Harvey, CFA, CIPM of CFA Institute did an excellent job emphasizing the key lessons learned as we near the 1-year mark of the adoption of the Marketing Rule. Below are some key takeaways worth noting:
Defining “Performance”
Since the Marketing Rule requires investment managers to present performance net-of-fees, it is important for firms to define what they consider “performance.” The SEC takes a straightforward approach, generally considering any statistic that demonstrates how much an investor earned from an investment to be performance. But, even with this simple and easy to understand approach, there can be some grey areas.
Based on the discussions in this session, it seems to now be widely accepted that in addition to basic returns being considered performance that contribution is also considered performance, while attribution and most performance appraisal measures are not considered performance. Performance appraisal measures should be individually considered to confirm if they are demonstrating the amount earned (which would be performance) or if it is used as a measure of the manager’s skill(which would not be considered performance).
Some portfolio characteristics could also be a grey area that firms should be careful to consider before presenting solely as gross-of-fees. For example, yield was discussed at length. It was said that total portfolio yield for something like an enhanced cash portfolio likely would be performance because the yield in that case is essentially the return the investor earned. On the other hand, dividend yield for a growth strategy where this does not directly indicate the amount the investor earned *might* be performance. This really would come down to how it is presented and how material the yield is to the strategy. If material to the strategy’s return, this may be considered performance and, in this case, would need to be reduced by a model fee.
After determining that a statistic is not performance and will be presented based on gross-of-fee input data, it is important to clearly label these figures as gross. A disclosure under the table or chart that simply states something like, “Risk statistics are presented gross-of-fees,” should suffice.
There was also a lot of discussion relating to applying fees to extracted performance such as sector and holdings-level performance. It was made very clear that each segment must be reduced and presented net-of-fees so fees cannot just hit the cash segment or something like that. To achieve this, most firms are using a model fee. For example, if the highest fee for the strategy is 1% per year and quarterly sector returns are presented, each sector’s quarterly return is reduced by 0.25%.
Hypothetical Performance
Hypothetical performance has been a focus of the initial SEC enforcement actions taken against firms under the Marketing Rule. The main issue has been firms broadly distributing hypothetical performance without any policies and procedures in place to ensure the distribution of this type of performance is limited only to those that can be reasonably expected to understand it.
The key is that firms must document policies that clearly define the intended audience for a particular presentation of hypothetical performance and then ensure that the presentation only goes to this audience. In addition, documentation should include the tools necessary to understand the information provided. For example, the type of hypothetical performance should be clearly described as well as any assumptions made to create this performance.
Hypothetical performance is very broadly defined. It could be anything from a back-tested model to a paper portfolio or even just an aggregation of extracted returns (e.g., a composite of carveouts). It should be clear what the performance represents and consideration should be given to the complexity of the information, especially when determining it’s appropriate audience.
Private Fund Adviser Quarterly Statement Rule
Anne Anquillare, CFA, Head of US Fund Services with CSC Global Financial Markets and Pamela Grossetti, Partner with K&L Gates together with Krista Harvey, CFA, CIPM of CFA Institute walked us through the key elements to prepare for with the new Private Fund Adviser Quarterly Statement Rule. Below are some key takeaways worth noting:
The Compliance Date for the Quarterly Statement Rule is March 14, 2025. This may sound like a long time away, but it is important to keep in mind that the requirement to include cross-references to the underlying governing documents in the Quarterly Statement may require amendments to such documents before the first Quarterly Statement is issued, and this could be time consuming.
Under this new rule, private fund managers must distribute a quarterly statement to the investors in the fund within 45 days after each quarter ends and 90 days after year-end. This is required for any private fund that has at least two full quarters of operating results.
There are many items that must be included in the quarterly statements relating to general fund details like fees and expenses as well as disclosures that are cross-referenced to the private fund’s offering documents; however, being the GIPS conference, this presentation was primarily focused on the performance requirements.
The performance requirements for liquid funds are very different for illiquid funds. An illiquid fund is one that is not required to redeem interests when requested by an investor and has limited opportunities for an investor to withdraw funds prior to the fund’s termination. If a fund manager determines that their fund is liquid, the performance requirement for the quarterly statement is limited to showing the following three items, each in equal prominence:
- Annual net-of-fee returns for each of the past 10 fiscal years (or back to inception if shorter)
- Annualized net-of-fee returns for the past 1, 5, and 10 years through the end of the latest fiscal year (or since inception if shorter)
- Year-to-date net-of-fee return for the current fiscal year
Illiquid funds have a much more significant requirement with 12 figures they are required to present:
Portfolio-Level
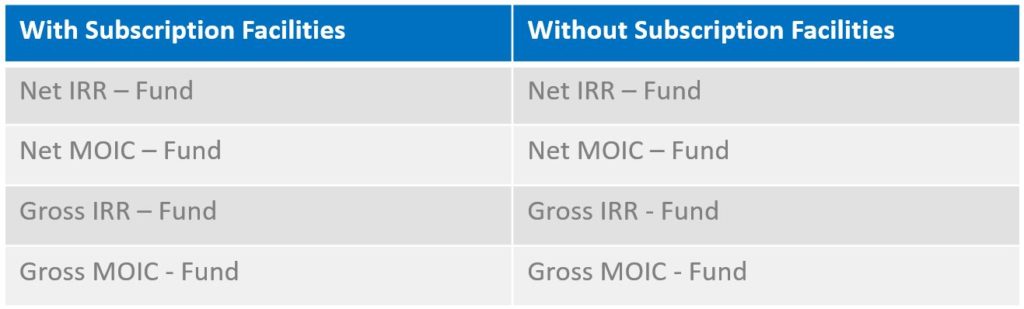
Investment-Level

Unlike the GIPS Standards, under this rule, there is no exemption for funds that only use a subscription line of credit for a short period of time. Funds that utilize a subscription line of credit for any period are required to show the metrics listed above both with and without the subscription line.
Another notable difference from the GIPS standards is that this rule requires interest expense charged from the subscription line of credit to be added back when calculating the “without subscription line of credit” version of the required metrics. The GIPS standards do not require this adjustment.
It was also discussed that if these quarterly statements were provided to prospective investors instead of only current investors then they would also need to be reviewed to confirm that they meet the Marketing Rule on top pf the Quarterly Statement Rule.
Current State of SEC Exams
Mark Dowdell, Assistant Regional Director with the SEC together with Ken Robinson, CFA, CIPM from CFA Institute discussed current trends in SEC examinations. Below are some key takeaways worth noting:
There was a strong emphasis on the need for clear policies and procedures that have been customized for the firm. Specifically, it was emphasized that policies and procedures relating to hypothetical performance are not the only thing firms should make sure they add for the Marketing Rule. For example, if firms are presenting predecessor performance or extracted performance there should be documented policies for this as well.
It was mentioned that in addition to standard examinations, the SEC is also conducting some risk-based exams that may be limited in scope, but go very deep on a narrow area. This may even include the recalculation of performance in their own systems to get comfortable with the accuracy of presented figures.
Outside of the recent enforcement actions relating to hypothetical performance, the SEC continues to see firms make exaggerated or untrue statements relating to the number of staff they employ, the qualifications of staff, awards received, the use of AI in the investment process, and their adherence to ESG standards in the investment process. While it is okay to state opinions in marketing materials, statements of fact absolutely must be substantiated.
Developing a Database Strategy
Jill Banaszak, Global Head of Omni Success at eVestment lead a great session on getting the most out of 3rd party and consultant databases.
The most important takeaway was the importance of using databases to tell the story of your firm in a complete and accurate way. Often firms leave a number of fields blank or neglect to revisit (or update) the narrative sections to remain accurate and in sync with their other messaging online or in marketing materials. Asset owners and their representatives use the databases to make short lists of firms meeting their criteria and many firms end up excluded as a result of blank fields or inconsistencies in messaging. At a minimum, firms should target completing at least 80% of the requested information.
It is also important to ensure information is completed timely and accurately. Firms should have monthly figures updated by the 12th business day of the month at the latest to avoid missing out on searches. To avoid errors or incomplete information, firms should consider who is tasked with updating the information and also ensure this person or team is qualified and has access to all relevant information so it can be fully completed. Implementing a quality control process to double check the information is also important to avoid typos or other mistakes in the information presented.
Applying the GIPS Standards to OCIOs
There is currently an exposure draft of the Guidance Statement for OCIO Strategies out for public comment with comments due by 20 November 2023. This session was led by a group of panelists who were part of the OCIO working group that created this new guidance statement. The purpose of this guidance statement is to improve comparability between OCIO strategies. The primary change in this proposed guidance that deviates from the current requirements of the GIPS standards for firms is the required composite structure that all OCIO managers would need to follow.
The required composite structure would separate liability-focused composites from total return objective composites and would then further break the composites down by their allocation between risk mitigating assets and growth assets ranging from conservative to aggressive allocations. There are specific weightings defined for each that are intended to line up with commonly used OCIO benchmarks.
These new composites are only required to build out five years of history, but like other composites firms manage, must then build up to showing a ten year track record before any performance periods can be removed.
This guidance statement also proposes requiring both gross-of-fee returns and net-of-fee returns instead of only one because of the complexity of OCIO fees.
This guidance statement has not yet been officially adopted, but once approved, it is expected to allow for a 12-month implementation period for firms to update their policies and procedures, construct composites that align with the prescribed composite structure, and create GIPS reports for these new composites.

Conclusion
This year’s speakers did a great job providing clarification on the SEC Marketing Rule and other relevant topics that impact GIPS compliance and investment performance.
We were happy to see many old friends in person this year in Chicago and look forward to seeing everyone again next year in San Diego. It was announced that next year’s conference will be held on the 17th – 18th of September in San Diego, California!
If you have any questions about the 2023 GIPS Standards Conference topics or GIPS and performance in general, please contact us.
*A previous version of this article included a mistake for investment-level figures for illiquid funds. This has been corrected.

